html_dom
HTML
DOM
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page, the HTML DOM model is constructed as a tree of Objects
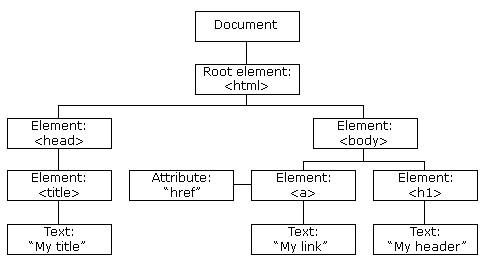
Everything in the DOM is a node(text can be a node as well)
1 | <!--document node--> |
The HTML DOM is a standard object model and programming interface for HTML. It defines:
- The HTML elements as objects
- The properties of all HTML elements
- The methods to access all HTML elements
- The events for all HTML elements
Document object
The document object represents your web page, it’s root node of the tree, Here are methods commonly used.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| document.getElementById(id) | Find an element by element id |
| document.getElementsByTagName(name) | Find elements by tag name |
| document.getElementsByClassName(name) | Find elements by class name |
| element.setAttribute(attribute, value) | Change the attribute value of an HTML element |
| document.createElement(element) | Create an HTML element |
| document.removeChild(element) | Remove an HTML element |
| document.appendChild(element) | Add an HTML element |
| document.replaceChild(new, old) | Replace an HTML element |
| document.write(text) | Write into the HTML output stream |
| document.getElementById(id).onclick = function(){code} | Adding event handler code to an onclick event |
Some attributes of document root you should know
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| document.anchors | Returns all <a> elements that have a name attribute |
| document.cookie | Returns the document’s cookie |
| document.forms | Returns all <form> elements |
| document.images | Returns all <img> elements |
| document.links | Returns all <area> and <a> elements that have a href attribute |
| document.title | Returns the <title> element |
| document.URL | Returns the complete URL of the document |
element object
Find an element through Document object or another element, if the method is called under an element, it checks child of that element, not root.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| element.getElementById(id) | Find an element by element id |
| element.getElementsByTagName(name) | Find elements by tag name |
| element.getElementsByClassName(name) | Find elements by class name |
| element.hasAttributes() | Return true if has any attribute |
| element.hasAttribute(“class”) | Return true only if has such attribute |
| element.setAttribute(attribute, value) | Change the attribute value of an HTML element |
| element.removeAttribute(attribute) | Remove a particular attribute |
| element.hasChildNodes() | Return true if has at least one child |
| element.insertBefore(new, exist) | Insert child before another existed child |
| element.removeChild(element) | Remove an HTML element |
| element.appendChild(element) | Add an HTML element |
| element.replaceChild(new, old) | Replace an HTML element |
| document.write(text) | Write into the HTML output stream |
| element.getElementById(id).onclick = function(){code} | Adding event handler code to an onclick event |
| element.addEventListener(“click”, click_handler) | Adding event handler for click event |
| element.removeEventListener(event_listener) | Removing event listener |
| element.querySelector(“p.intro”) | Return first element by CSS selector |
| element.querySelectorAll(“p.intro”) | Return all elements by CSS selector |
| element.focus() | Get focus |
add a new element
1 | <div id="div1"> |
Attribute for element
| attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| element.attributes | Return all attributes |
| element.className | Return value of ‘class’ attribute |
| element.id | Return Id attribute |
| element.innerHTML | Return inner HTML |
| element.innerText | Only return value of ALL Text nodes include children |
| element.nodeName | Return tag name like p, iframe |
| element.parentNode | Return parent node |
| element.firstChild | Return first direct child node |
| element.lastChild | Return last direct child node |
| element.nextSibling | Return next sibling node |
| element.previousSibling | Return previous sibling node |
| element.childNodes | Return direct child nodes |
| element.style.property | Set/Return css style |
Event
Event object is passed to event handler when event happens, actually the passed event is not only Event object, but more specific one which is child of Event object, more specific means more meta data about the event, here is the inheritance of events
Event object has below attribute
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| bubbles | Return True if event is bubble event |
| currentTarget | Return current Listener target |
| target | Return element who triggered such event |
| type | return type of event |
More specific events, refer to Events API.
Note: as event could bubble, hence currentTarget may not be target
There are two ways to add event handler, but addEventListener() method attaches an event handler to an element without overwriting existing event handlers. You can add many different types of event handlers to one element. You can also add many event handlers of the same type to one element, i.e two “click” events.
The addEventListener() method makes it easier to control how the event reacts to bubbling.
1 | // function only takes event object as the input or nothing |
1 | <!-- |
NodeList vs HTMLCollection
A NodeList object is a list (collection) of nodes extracted from a document, while HTMLCollection is only for HTML element(tag), NodeList is for inner text as well which is also a node object.
HTMLCollection returned
- getElementsByTagName()
- getElementsByClassName()
NodeList returned
- All browsers return a NodeList object for the property childNodes.
- Most browsers return a NodeList object for the method querySelectorAll()
Same
- Both an HTMLCollection object and a NodeList object is an array-like list (collection) of objects.
- Both have a length property defining the number of items in the list (collection).
- Both provide an index (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …) to access each item like an array.
Different
- HTMLCollection items can be accessed by their name, id, or index number.
- NodeList items can only be accessed by their index number.
- Only the NodeList object can contain attribute nodes and text nodes.
BOM
The Browser Object Model (BOM) allows JavaScript to “talk to” the browser, it’s information about browser, it has several objects to represent such info
- window
- window.screen or screen for short
- window.location
- window.history
- window.navigator
JQuery
jQuery was designed to handle Browser Incompatibilities and to simplify HTML DOM Manipulation, Event Handling, Animations, and Ajax, it depends on Dom native API above.
JQuery uses CSS selector to find element
1 | //import jquery first. |
Operation(API) on the selected element
- .text get/set the content of selected element $(“#bsd”).text(“new”);
- .html get/set the entire html of selected element $(“#bsd”).html()
- .before add a html element(with tag) before the selected element
- .after add an element after the selected element
- .append add a html element(with tag) inside the selected element
- .attr get/set the given attr of an html element $(“#bsd”).attr(“given_attr”) $(“$bsd”).attr(“given_attr”, “given_value”);
- .css get/set the style of the selected elements
- .parent get the parent element of the selected element $(“#bsd”).parent().
- .each callback on each of the selected groups($(“a”), $(“.className”);
AJAX
.ajaxSetup()
set defaults for AJAx-related parameters such as caching, methods, error handling, among others, this is used for all AJAX call, also you can set them separately by .ajax()
All subsequent Ajax calls using any function will use the new settings, unless overridden by the individual calls, until the next invocation of $.ajaxSetup().
.ajax() parameters are map with key:value, specify method(GET,POST etc) the url, callback functions when error, successful, data type and data cache response etc!!
1 | load() get() post getJson() |
1 | function successFun(data, status) { |