docker-frequently-used-commands
Docker CLI
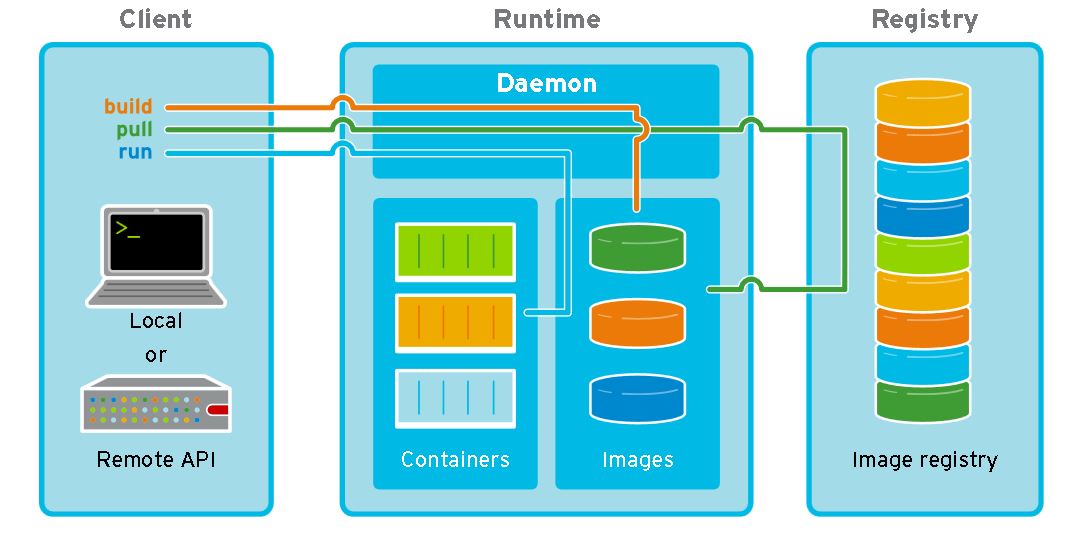
Before going into docker cli, let’s see how docker client, daemon and registry works, here is an overview of these parts and how they work with each other.
As you can see client, daemon, registry are three different parts, they can run in one machine or different machines, by default, daemon listens on Unix socket, CLI connects with that socket, registry can be your company registry or docker official hub,
You can use docker cli or call REST API to communicate with docker daemon, docker cli is just a wrapper of rest api
All docker commands are available here
Container
Frequently used one
1 | # run with bridge mode(vethpair) with specific address |
Run a container in interactive mode with tty
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12# docker run = docker create + docker start
# -t: Allocate a pseudo-TTY, When set to true Docker can allocate a pseudo-tty and attach to the standard input of any container
# -i: Keep STDIN open even if not attached.
$ docker run -it nginx bash
# this will pull nginx(image) and create a container and start it with bash command
# Note: bash overwrite CMD provide in nginx so nginx daemon is not started in this docker
$ docker run --rm -it nginx bash
control + C
# --rm means this docker will be removed when it exited
$ docker ps -a # will not show it as it's removedRun a container in detached mode or non-detached mode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8# detach(run in background) then later on you attach to it
$ docker run --name my-nginx -d nginx
$ docker attach $container_id
# OR
$ docker run nginx
# both will run nginx image from CMD provided in docker image CMD ["nginx" "-g" "daemon"]
# as docker run will create container if not exist(user docker create) so it's also
# has lots of args like create provide https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/run/Check start logs of a specific container
1
2
3
4$ docker logs $container_id(name)
# if docker failed to write such log, check syslog as well
# /var/log/syslogList containers and its disk usage
1
2
3
4$ docker ps # only active containers
$ docker ps -a # all containers even it's stopped.
$ docker ps --size
$ docker stats # show running stats CPU, MEM, IO, NETcreate/stop/start/restart/rm container
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8$ docker create --name my-nginx nginx
$ docker start $container_id(name)
$ docker stop $container_id(name)
$ docker restart $container_id(name)
$ docker rm $container_id(name)
# Actually create provides lots of args when create a docker to set it config
# like volume, mount points, cpu, entrypoint, CMD, env etc
# https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/create/Run a new command in an running container
1
$ docker exec -it $container_id(name) bash
copy file in/out container
1
2$ docker cp $container_id(name):/home/text.txt /root/text.txt
$ docker cp /root/text.txt $container_id(name):/home/text.txtinspect a container
1
$ docker inspect $container_id
Image
- pull an image from registry
1
$ docker pull nginx:latest
- build an image
Details refer to Dockfile inside - check history of an image
1
2
3$ docker history $image_id
# OR to show history full description
$ docker history $image_id --no-trunc - list images
1
$ docker images
- remove image(s)
1
$ docker rmi $image_id
- tag an image
1
2$ docker tag $image_id $new_image_tag # will create a new image
$ docker images - create an image from a running container
1
$ docker commit $container_id $new_image_name # add the image to local repo
- backup/restore an image
1
2
3
4# save an image to tar file
$ docker save nginx:latest >/root/back.tar # must be absolute path with repo and tag later on when load
# still have such info
$ docker load </root/back.tar # must be absolute pathNetwork
1
2$ docker network ls
$ docker network inspect $network_id
Registry
1 | $ docker search xxx # search image from registry |
Volume
1 | $ docker volume ls |
Others
- check docker info
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33$ docker info
Client:
Context: default
Debug Mode: false
Plugins:
app: Docker App (Docker Inc., v0.9.1-beta3)
buildx: Docker Buildx (Docker Inc., v0.8.2-docker)
scan: Docker Scan (Docker Inc., v0.17.0)
Server:
Containers: 0
Running: 0
Paused: 0
Stopped: 0
Images: 0
Server Version: 20.10.15
Storage Driver: overlay2 ------important
Backing Filesystem: xfs
Supports d_type: true
Native Overlay Diff: true
userxattr: false
Logging Driver: json-file -------important
Cgroup Driver: cgroupfs
Cgroup Version: 1
...
Docker Root Dir: /var/lib/docker -----important
Debug Mode: false
Registry: https://index.docker.io/v1/
...
$ docker version